Going public is one of the big turn points in the life cycle of a company. Generally, it refers to issuing shares through an exchange to transform a private business into a public one. It has been called an initial public offering or IPO. It opens up new
avenues for growth, capital, and publicity but demands strict regulations and
complexities on the other hand. Here's an SEO-friendly guide on the major steps and considerations to go public.
Is an IPO a Good Sense for Your Firm?
It is worth determining whether the act of pursuing an IPO is part and parcel of your
long-term goals of the company. An IPO subjects you to intense reporting requirements and shareholder oversight, which will transform not only your company's strategy but even the way you run the business.
Advantages:
• Higher influx of capital; higher brand recognition; higher acceptability.
• Higher regulatory scrutiny, costs and loss of control to the shareholders.
Create an Experienced IPO Team
The process of taking a company public requires an experienced team of experts whose experience will be depended upon to determine some of the legal, financial, and several operational decisions that will be made. Your experienced IPO team should consist of :
Investment Bankers: They underwrite the IPO, set up the IPO's original share price, and help in selling those shares.
Legal Counselors: The Company would require lawyers that will ensure all
applicable government regulation and other rules are being adhered to and coordinating with the SEC as much as the necessary filing.
Accountants: Strict accounting needs to be maintained as well as the hiring of auditors that would be providing prepared financial statements.
Financial Statements and Audits

Your company must show it is open to prospective investors' access to thorough financial records. The term includes:
Audited Financial Statements: The SEC requires that several years of audited
financial statements must exist, which is to say some accounting by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
Financial Projections: In a word, some kind of clarity or projection about potential future revenue, expense, and growth will make things clear enough to the investors.
File with the SEC
Going public is one of the major steps in filing a registration statement with the SEC. S-1, effectively, gives potential investors all the information they might want to know about the company's business model, finance, and even its management team.
SEC Review:
The SEC analyzes the registration statement to verify that the details provided to investors are clear and understandable. A lot of criticism and revision might occur before approving the IPO.
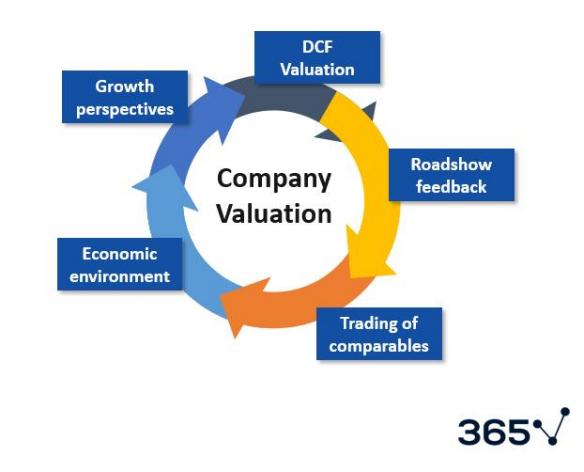
Determine Your IPO Price
The interest of the issuer should also be taken into account along with that of the future shareholders by the IPO pricing. I believe that it is through your investment banking team which is best positioned in getting to figure out the perfect price for which the shares should be priced when there is consideration of the value of the company, the prevailing market conditions, as well as investor demand.
Roadshow: Institutional investors are informed about the IPO much in advance of the
date the offer opens through a promotional tour, also known colloquially as a
roadshow. This is one of the main steps considered to gauge demand and to come up with a firm share price.
IPO Launch
The public is given the opportunity to purchase shares on the day of the IPO. This stock then commences trading on that exchange chosen by the company. Opening
day for trading is usually one of the most critical because it will set the tone for everything else about the stock. Events on IPO Day: Usually an offering by the investment banks taking part in the transaction. The firm's CEO and other
management typically attend, and even sometimes ring the opening bell at the stock exchange.
Manage Investor Relations
Going public will require managing relations with shareholders and potential investors,
thus retaining investor confidence. A public company must have an effective
communication system with its stakeholders and should retain transparency about its performance and strategy.
Investor Relations Team: Apart from updating the shareholders constantly through
the investor relations team, which manages the public face of the company, the
venture should be sanctioned because it would keep communication constant about the growth and public face of the company.
Growth Focus
No doubt that source of capital would soon come; however, long-term growth and profitability are the keys to steady performance. Excellent strategic planning is
essential for a publicly traded company to fulfill quarterly expectations on earnings.
Conclusion
Taking a company public is not too-straightforward, but it's very rewarding. From making financial statements ready to actual adherence to SEC regulations, it's almost a thinking-out-loud kind of process that is followed up with expert advice.
Going public would certainly give your company access to much-needed capital for scaling, but it does involve more responsibilities and pressures. A powerful team, the requirement of the law, and fulfilling the demand of the shareholder equity will be
your company's guarantee for going out of the process with an IPO as successful and functioning publicly.



